Most Commented
Medical Robotics Course




Description material
Published 9/2023
MP4 | Video: h264, 1280x720 | Audio: AAC, 44.1 KHz
Language: English | Size: 4.41 GB | Duration: 4h 46m
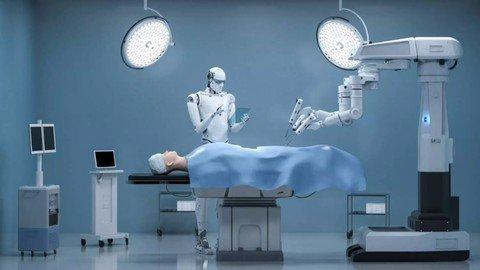
Unlock the Future of Healthcare with Advanced Skills and Expertise
What you'll learn
Medical robotics is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling minimally invasive surgeries, precision medicine, and enhanced patient care.
The demand for medical robotics expertise transcends borders, providing opportunities for work and research on an international scale.
Gain the skills to design, develop, and operate robotic systems for medical applications, contributing to innovation in the healthcare sector.
Learning this field equips individuals to be part of this transformative process.
Requirements
To pursue a Medical Robotics Course, you typically need: Educational Background: A bachelor's degree in a relevant field (engineering, computer science, medicine, etc.). Prerequisite Knowledge: Some courses may require a foundation in robotics, programming, or biology. GRE Scores: For international students applying to universities abroad. English Language Proficiency: Proof of English language proficiency (TOEFL/IELTS) for non-native speakers. Letters of Recommendation: Usually two to three letters from professors or professionals in the field. Statement of Purpose: A compelling essay outlining your motivations and goals. Interview: Some institutions may require an interview as part of the admission process.
Description
Overview:In an era of rapid technological advancement, the field of healthcare is not far behind in embracing innovation. One such groundbreaking innovation is medical robotics. The fusion of medicine and robotics has paved the way for cutting-edge treatments, minimally invasive surgeries, and enhanced patient care. To harness the full potential of this field, a Medical Robotics Course has become essential. In this blog, we delve into the significance of such a course, its benefits, eligibility, requirements, key features, and the importance of certification.Benefits of Learning Medical Robotics:Revolutionizing Healthcare: Medical robotics has revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling precise, minimally invasive procedures, leading to faster recovery times and reduced patient discomfort.Career Opportunities: Learning medical robotics opens up diverse career opportunities. Graduates can work as robotic surgeons, biomedical engineers, researchers, or even educators.Innovation Hub: The course fosters innovation, encouraging students to develop new robotic technologies to address healthcare challenges.Improved Patient Outcomes: Medical robotics ensures accuracy and precision, resulting in improved patient outcomes and a lower risk of complications.Who Can Learn:Medical Professionals: Surgeons, doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals looking to enhance their skills and embrace technology in their practice.Engineers: Those with a background in mechanical, electrical, or biomedical engineering interested in applying their knowledge to healthcare.Students: Aspiring students seeking a career in healthcare or robotics can also enroll to gain a competitive edge.Requirements To Study:Educational Background: Typically, a bachelor's degree in a relevant field like medicine, engineering, or biology is required. Some courses may have specific prerequisites.Technical Skills: Basic knowledge of programming, mathematics, and computer science can be beneficial.Hardware and Software: Access to the necessary hardware and software for hands-on learning and simulations.
Overview
Section 1: Module 1: Introduction to Medical Robotics
Lecture 1 About Robot and Why. Part 1
Lecture 2 What is Robotics Terminology. Part 2
Lecture 3 Surgical Robots. Part 3
Lecture 4 Telepresence Robots. Part 4
Lecture 5 The Exoskeleton Devices. Part 5
Lecture 6 Role in Modern Medicine. Part 6
Lecture 7 Mechanical Robots. Part 7
Lecture 8 Robots in Clinical Diagnosis and Epidemic Control. Part 8
Lecture 9 Types of Medical Robots. Part 9
Lecture 10 Main Type of Robotic Operating System, Part 10
Lecture 11 Intellifill I.V. Pharmacy Robot. Part 11
Lecture 12 Remote Presence RP-7. Part 12
Lecture 13 Balance Training Assist. Part 13
Lecture 14 Microbots. Part 14
Lecture 15 Cosmobot, CODY, and RP-VITA. Part 15
Section 2: Module 2: Fundamentals of Robotics in Medicine
Lecture 16 What Are The Parts of a Robot. Part 1
Lecture 17 Robot Characteristics. Part 2
Lecture 18 Advantage Vs Disadvantage of Robots. Part 3
Lecture 19 Robotics in Healthcare. Part 4
Lecture 20 Robotics Kinematics. Part 5
Lecture 21 Role in Precise Medical Procedures. Part 6
Lecture 22 Economics in Medical Robotics Design. Part 7
Lecture 23 Backgroung on Medical Robotics. Part 8
Lecture 24 MIS Robot. Part 9
Section 3: Module 3: Human Vs Robot
Lecture 25 Human - Robot Relationships. Part 10
Lecture 26 Human - Robot Collaboration. Part 11
Lecture 27 Physical Human - Robot Interaction. Part 12
Lecture 28 Teleoperation and Haptic. Part 13
Section 4: Module 4: Medical Imaging and Navigation
Lecture 29 Medical Imaging Timeline. Part 1
Lecture 30 Electromagnetic Spectrum. Part 2
Lecture 31 Contrast. Part 3
Lecture 32 X-Ray Modalitirs, X-Ray Contrast, Imagine Basic Production. Part 4
Lecture 33 Radiography. Part 5
Lecture 34 X-Ray Computed Tomography(CT). Part 6
Lecture 35 CT Scanner & CT Slice Images. Part 7
Lecture 36 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Part 8
Lecture 37 Ultrasound (US) Imaging. Part 9
Lecture 38 Role of The Physicist in Diagnostic Radiology. Part 10
Lecture 39 Medical Physicist Skill. Part 11
Lecture 40 Robotic Technology in Medical Imaging. Part 12
Lecture 41 Image Guided Surgery (IGS). Part 13
Lecture 42 Benefits. Part 14
Section 5: Module 5: Case Studies
Lecture 43 Case Studies- Hematuria Protocol 3D CT. Part 15
Lecture 44 Coronary Artery Disease- Case 1. Part 16
Lecture 45 Coronary Artery Disease- Case II. Part 17
Section 6: Module 6: Surgical Robotics
Lecture 46 Robotic Surgical System- Da Vinci Surgical System. Part 1
Lecture 47 Significance of Da Vinci Surgical System. Part 2
Lecture 48 Robotic Assisted Surgery. Part 3
Lecture 49 Advantages and Disadvantage of Robotic Surgery. Part 4
Lecture 50 Myths About Robotic Surgery. Part 5
Section 7: Module 7: Types of Robotics Surgery
Lecture 51 Robotic Gynecologic Surgery. Part 6
Lecture 52 Robotic Prostate Surgery. Part 7
Lecture 53 Robotic Kideny Surgery. Part 8
Lecture 54 Robotic Colorectal Surgery. Part 9
Lecture 55 Single- Site Robotic Gallblader Surgery. Part 10
Lecture 56 Why Robotic Surgery is a Better Option. Part 11
Lecture 57 Simulation in Robotic Surgery. Part 12
Section 8: Module 8: Future Trends
Lecture 58 Emerging Trends. Part 1
Lecture 59 UltraSound Imaging. Part 2
Lecture 60 Custom Design Robots. Part 3
Lecture 61 Commercial Robots. Part 4
Lecture 62 Collaborative Assistance. Part 5
Lecture 63 Autonomous Systems. Part 6
Section 9: Module 9: Nano-Robots
Lecture 64 Nano-Robots. Part 7
Lecture 65 Challenges in Building Nanobots. Part 8
Lecture 66 Medical Application of Nano-Robotics Systems. Part 9
Lecture 67 Nanobots For Cancer Treatment. Part 10
Lecture 68 Nanobots Market Dynamics. Part 11
Lecture 69 Benefits of Medical Robots. Part 12
Lecture 70 Future of Nanobots. Part 13
Lecture 71 Swarn Robotics. Part 14
Section 10: Module 10: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Lecture 72 Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Part 15
Lecture 73 Diagnosis and Treatment Applications. Part 16
Lecture 74 Challenges for Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Part 17
Lecture 75 Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Part 18
Section 11: Module 11: Ethical Considerations
Lecture 76 Robotics Regulatory Trends. Part 19
Lecture 77 Medical Ethics. Part 20
Lecture 78 Significance of Da Vinci Surgical System. Part 21
Students and Enthusiasts: With a passion for technology and a desire to make a difference in healthcare.,Computer Scientists: Interested in the development of robotic systems.,Mechanical and Electrical Engineers: Interested in specializing in medical applications.,Medical Professionals: Doctors and nurses interested in leveraging technology for better patient care.,Biomedical Engineers: Seeking to apply engineering principles to healthcare.
Buy Premium Account From My Download Links & Get Fastest Speed.
https://ddownload.com/cn2ngb7sydd5/Medical_Robotics_Course.part1.rar
https://ddownload.com/azoezoenv9nc/Medical_Robotics_Course.part2.rar
https://ddownload.com/kn2o3af01qbo/Medical_Robotics_Course.part3.rar
https://ddownload.com/59nd8ll1p7u7/Medical_Robotics_Course.part4.rar
https://ddownload.com/xychu4ujbn9a/Medical_Robotics_Course.part5.rar
https://rapidgator.net/file/66882c50e3a16dc71c3cd8831cc22628/Medical_Robotics_Course.part1.rar.html
https://rapidgator.net/file/8c89789dbf9045470a573c03efaa415b/Medical_Robotics_Course.part2.rar.html
https://rapidgator.net/file/10fe7cda281c7ef821d84297202d81d4/Medical_Robotics_Course.part3.rar.html
https://rapidgator.net/file/2fd369e2a0f9868f6599b2350750a970/Medical_Robotics_Course.part4.rar.html
https://rapidgator.net/file/3510eb468b60f32f39a49595207521ad/Medical_Robotics_Course.part5.rar.html
Join to our telegram Group
Information
Users of Guests are not allowed to comment this publication.
Users of Guests are not allowed to comment this publication.
Choose Site Language
Recommended news
Commented


![eM Client Pro 9.2.1735 Multilingual [Updated]](https://pikky.net/medium/wXgc.png)





![Movavi Video Editor 24.0.2.0 Multilingual [ Updated]](https://pikky.net/medium/qhrc.png)

