Most Commented
Intermediate System-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Zero-to-Hero




Description material
Published 3/2023
Created by Arash Deljoo
MP4 | Video: h264, 1280x720 | Audio: AAC, 44.1 KHz, 2 Ch
Genre: eLearning | Language: English | Duration: 34 Lectures ( 14h 19m ) | Size: 5.66 GB
Concepts , Configuration , Optimization
What you'll learn
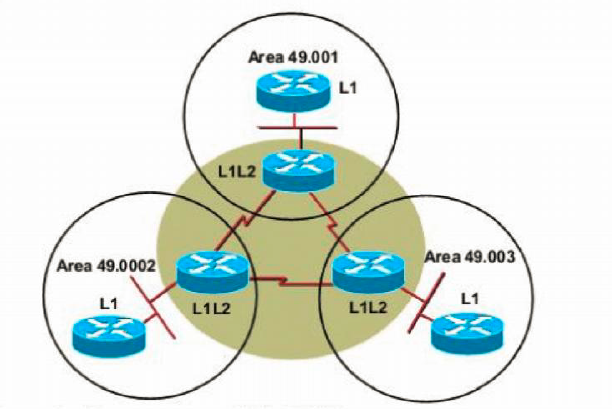
The History of IS-IS
CLNP[ Connection Less Network Protocol ]
IS-IS Fundamentals
IS-IS Process and Terminology
IS-IS Basic Configuration , Verification
IS-IS Topology and Database Analyzing
IS-IS Neighborship Conditions
IS-IS Broadcast Network Type
IS-IS Operation Over Point-to-Point Links
IS-IS Operation Over Broadcast Links
IS-IS Propagating LSPs on a Point-to-Point Interface
IS-IS Propagating LSPs on a Broadcast Interface
IS-IS LSP , CSNP , PSNP Authentication
IS-IS Metric
IS-IS Equal Cost Multi Path[ECMP]
IS-IS Default Route Advertisement
IS-IS Summarization & Route-Leaking
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - SPF Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - PRC Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - LSP Generation Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - LSP Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - LSP Retransmit-Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - LSP Retransmit-Throttle-Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - LSP Refresh Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Max LSP Lifetime
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - CSNP Interval
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Advertise Prefix
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Advertise Passive Only
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - incremental SPF (iSPF)
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Protocol Shutdown
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - LSP Full Suppress
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Fast Flood
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Hello Padding
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Set-Attached-bit
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Set-Overload-bit
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Max Area Address
IS-IS Optimization and Timers - Tag
IS-IS IPv6 Routing - Single Topology vs Multi Topology
Requirements
You need to have routing fundamentals knowledge up to CCNA level . You can implement all scenarios of this course in GNS-3 and EVE-NG Emulators.
Description
The IS-IS (Intermediate System - Intermediate System) protocol is one of a family of IP Routing protocols, and is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) for the Internet, used to distribute IP routing information throughout a single Autonomous System (AS) in an IP network.IS-IS is a link-state routing protocol, which means that the routers exchange topology information with their nearest neighbors. The topology information is flooded throughout the AS, so that every router within the AS has a complete picture of the topology of the AS. This picture is then used to calculate end-to-end paths through the AS, normally using a variant of the Dijkstra algorithm. Therefore, in a link-state routing protocol, the next hop address to which data is forwarded is determined by choosing the best end-to-end path to the eventual destination.The main advantage of a link state routing protocol is that the complete knowledge of topology allows routers to calculate routes that satisfy particular criteria. This can be useful for traffic engineering purposes, where routes can be constrained to meet particular quality of service requirements. The main disadvantage of a link state routing protocol is that it does not scale well as more routers are added to the routing domain. Increasing the number of routers increases the size and frequency of the topology updates, and also the length of time it takes to calculate end-to-end routes. This lack of scalability means that a link state routing protocol is unsuitable for routing across the Internet at large, which is the reason why IGPs only route traffic within a single AS.IS-IS was originally devised as a routing protocol for CLNP, but has been extended to include IP routing; the extended version is sometimes referred to as Integrated IS-IS.
Who this course is for
Enterprise Engineers , Service Provider Engineers , Data Center Engineers
Buy Premium Account From My Download Links & Get Fastest Speed.
https://1dl.net/i60lgbd2gjqp/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System___40_IS-IS__41__Zero-to-Hero.part1.rar
https://1dl.net/00uxv0hdyaht/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System___40_IS-IS__41__Zero-to-Hero.part2.rar
https://1dl.net/5phi0g9xncqg/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System___40_IS-IS__41__Zero-to-Hero.part3.rar
https://filerice.com/tg7ib5g8hpm5/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System_(IS-IS)_Zero-to-Hero.part1.rar
https://filerice.com/ybd6cbrqnfhi/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System_(IS-IS)_Zero-to-Hero.part2.rar
https://filerice.com/jjdo0s5fq8rv/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System_(IS-IS)_Zero-to-Hero.part3.rar
https://rapidgator.net/file/23b70dcd264b3adbf9b154eac0845659/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System_(IS-IS)_Zero-to-Hero.part1.rar.html
https://rapidgator.net/file/3933781e50a62aec01a01f65d7a13653/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System_(IS-IS)_Zero-to-Hero.part2.rar.html
https://rapidgator.net/file/5e4e6e9fb3c07cade8fe9dd0a9d8c843/Intermediate_System-Intermediate_System_(IS-IS)_Zero-to-Hero.part3.rar.html
Join to our telegram Group
Information
Users of Guests are not allowed to comment this publication.
Users of Guests are not allowed to comment this publication.
Choose Site Language
Recommended news
Commented


![eM Client Pro 9.2.1735 Multilingual [Updated]](https://pikky.net/medium/wXgc.png)






![Movavi Video Editor 24.0.2.0 Multilingual [ Updated]](https://pikky.net/medium/qhrc.png)

